9
Oct 08
Bitwise Operations
AND
A bitwise AND takes two binary representations of equal length and performs the logical AND operation on each pair of corresponding bits. In each pair, the result is 1 if the first bit is 1 AND the second bit is 1. Otherwise, the result is 0. For example:
0101
AND 0011
= 0001
XOR
A bitwise exclusive or takes two bit patterns of equal length and performs the logical XOR operation on each pair of corresponding bits. The result in each position is 1 if the two bits are different, and 0 if they are the same. For example:
0101
XOR 0011
= 0110
In Java, all integer types are signed, and the “<<” and “>>” operators perform arithmetic shifts. Java adds the operator “>>>” to perform logical right shifts, but since the logical and arithmetic left-shift operations are identical, there is no “<<<” operator in Java. These general rules are affected in several ways by the default type promotions; for example, since the eight-bit type byte is promoted to int in shift-expressions,[2] the expression “b >>> 2” effectively performs an arithmetic shift of the byte value b instead of a logical shift. Such effects can be mitigated by judicious use of casts or bitmasks; for example, “(b & 0xFF) >>> 2” effectively results in a logical shift.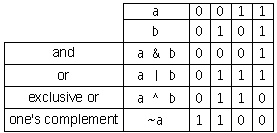
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.